Understanding DNS Lookup: How It Works and Why It Matters
Created on 24 September, 2025 • Checker Tools • 27 views • 2 minutes read
he internet as we know it wouldn’t function smoothly without the Domain Name System (DNS). Every time you type a website address into your browser, a process called DNS lookup takes place in the background.
The internet as we know it wouldn’t function smoothly without the Domain Name System (DNS). Every time you type a website address into your browser, a process called DNS lookup takes place in the background. This process translates human-readable domain names, like example.com, into machine-readable IP addresses. Without DNS lookup, we would be forced to memorize long sequences of numbers instead of simple names.In this article, we will explore what DNS lookup is, how it works, and why it’s so important for everyday internet use.
What is DNS Lookup?
A DNS lookup is the process of finding the IP address associated with a domain name. Since computers communicate through numbers (IP addresses), but humans prefer readable text (domain names), DNS acts as the bridge between the two.
When you enter a URL in your browser, your system doesn’t immediately know where that site lives. Instead, it must query DNS servers to retrieve the correct IP address. This is what allows you to connect to the website seamlessly.
Types of DNS Lookups
DNS lookups generally fall into two categories:
Forward DNS Lookup
A forward DNS lookup is the most common type. It translates a domain name (like google.com) into its corresponding IP address. This process is essential because your browser needs the IP address to establish a connection with the web server.
Reverse DNS Lookup
A reverse DNS lookup does the opposite. It starts with an IP address and tries to find the domain name linked to it. This is commonly used in network troubleshooting, spam filtering, and security verification.
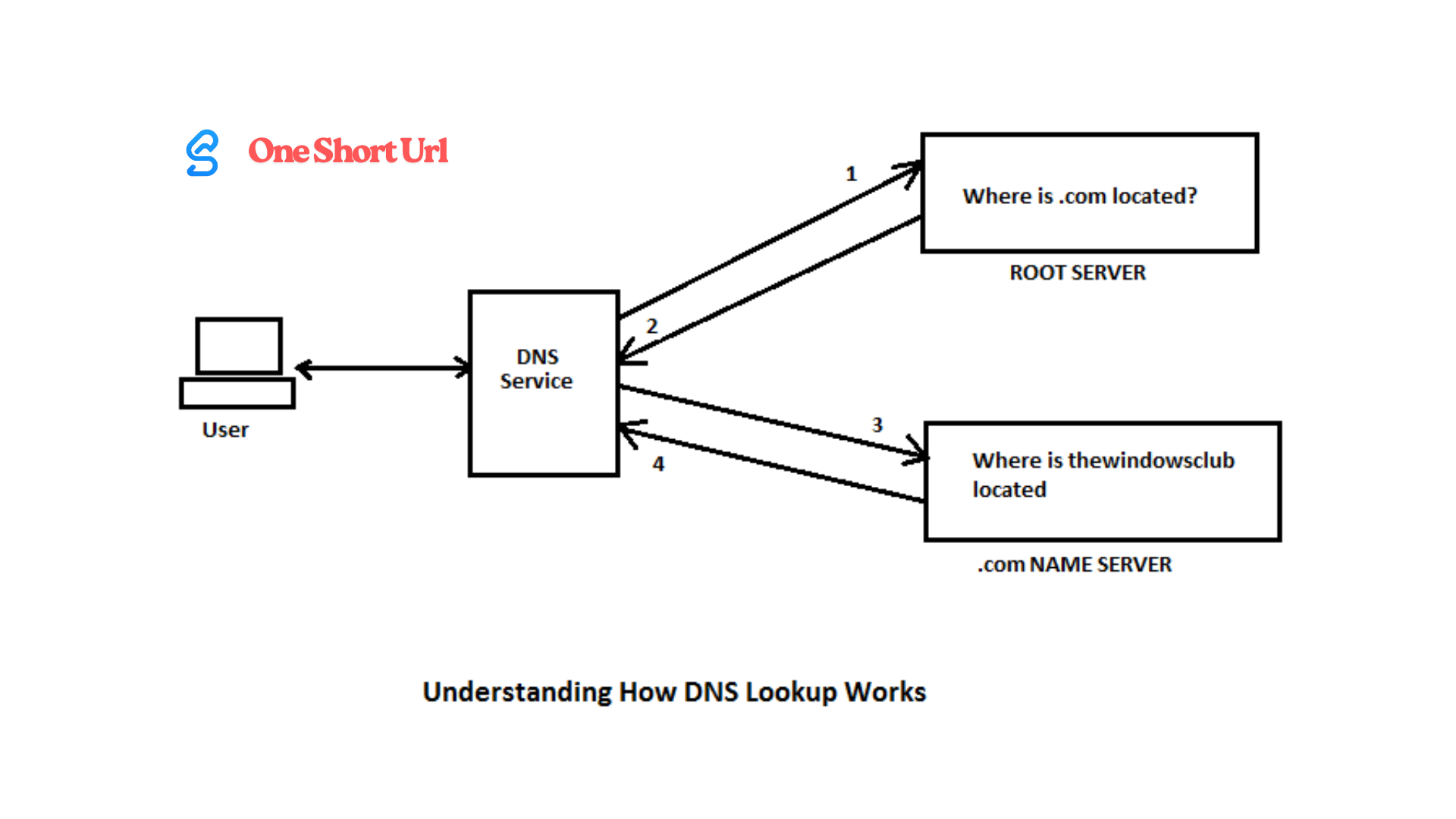
How DNS Lookup Works Step by Step
The DNS lookup process might seem instant, but it involves several steps:
User Request – You type a domain name into your browser.
Local Cache Check – Your operating system checks if the IP address is already stored locally.
Recursive Resolver Query – If not cached, the request goes to a DNS resolver (often provided by your ISP).
Root Server Query – The resolver asks a root DNS server where to find the domain’s authoritative server.
TLD Server Query – The resolver contacts the Top-Level Domain (TLD) server (e.g., .com, .net) for further direction.
Authoritative DNS Server Query – Finally, the resolver queries the authoritative server that holds the exact IP for the domain.
IP Address Returned – The resolver sends the IP back to your browser, which connects to the site.
This process usually takes milliseconds, thanks to caching systems that store results for faster access.
Why DNS Lookup Matters
DNS lookup plays a crucial role in internet functionality:
User Experience – Without it, browsing would be far more difficult.
Performance – Faster DNS lookups lead to quicker website loading times.
Security – DNS helps prevent phishing, spam, and malicious redirection through technologies like DNSSEC.
Reliability – DNS redundancy ensures that websites remain accessible even if some servers fail.
Common DNS Lookup Tools
If you want to check DNS records, several tools are available:
Command-Line Tools – nslookup, dig, and host are commonly used.
Online Tools – Websites provide easy DNS lookups for troubleshooting.
Monitoring Services – Advanced platforms help businesses track DNS health.
Final Thoughts
DNS lookup may be invisible to users, but it’s the backbone of how the internet operates. It transforms simple domain names into the numerical language that computers understand, ensuring smooth connectivity. Whether you are a casual web user or a network professional, understanding DNS lookup gives you valuable insight into how the web really works.
By appreciating the importance of DNS, you’ll not only enhance your technical knowledge but also be better prepared to troubleshoot and secure your online experience.